The sign() function returns the sign of its argument. It indicates whether its argument is positive, negative, or zero.
sign(number)
number.sign()
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)sign() accepts only numbers; it will not auto-convert Booleans or other data types.
Example Formulas
sign(-5) /* Output: -1 */
5.sign() /* Output: 1 */
sign(0) /* Output: 0 */
"-1".toNumber().sign() /* Output: -1 */
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Example Database
The example database below lists bank account balances. The sign() function is used to determine the output of the Status property.
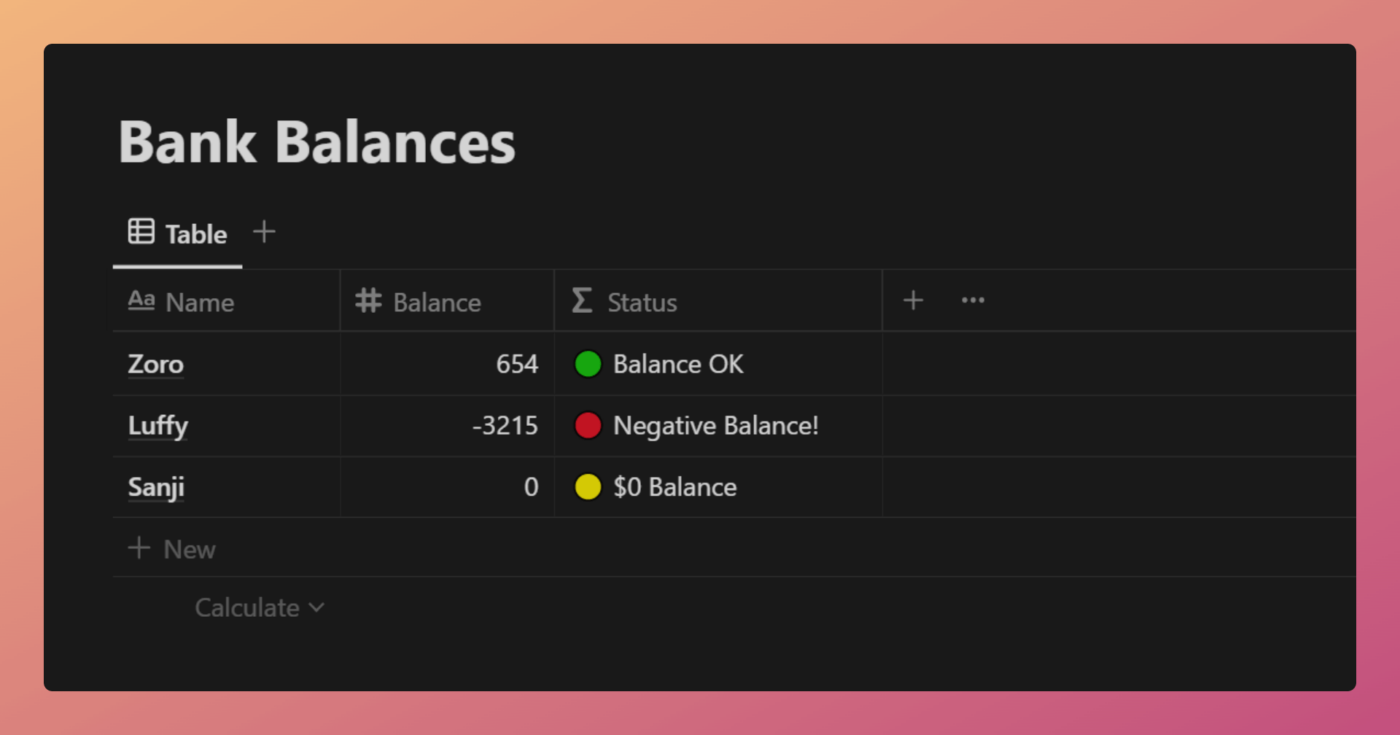
View and Duplicate Database

“Balance” Property Formula
ifs(
sign(
prop("Balance")
) == -1,
"🔴 Negative Balance!",
sign(
prop("Balance")
) == 0,
"🟡 $0 Balance",
"🟢 Balance OK"
)
/* Explained */
ifs(
/* Check if the sign value of Balance is -1 */
sign(
prop("Balance")
) == -1,
/* If so, display the following */
"🔴 Negative Balance!",
/* If not, check is the sign value of Balance is 0 */
sign(
prop("Balance")
) == 0,
/* If so, display the following */
"🟡 $0 Balance",
/* If not, display the following */
"🟢 Balance OK"
)
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)This simple formula uses an ifs to return one of three status messages. The output is determined by the sign() function’s output.
Good to know: You can also use comparison operators such as larger and smaller to accomplish the same thing.
E.g. prop("Balance") < 0.
Other formula components used in this example:






