The add (+) operator allows you to:
number + number
string + string
add(number, number)
number.add(number)
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Note that when using + with two different data types, they’ll both be converted to strings:
"It's " + now() /* Output: "It's @August 18, 2023 4:07 PM" */
1 + true /* Output: "1true" */
Code language: PHP (php)When used in mathematical equations, the + operator follows the standard mathematical order of operations (PEMDAS). For more detail, see Operator Precedence.
You can also use the function version, add(), though this version will only work with numbers.
Example Formulas
2 + 5 /* Output: 7 */
"Monkey D." + " Luffy" /* Output: Monkey D. Luffy */
add(4, 7) /* Output: 11 */
4.add(7) /* Output: 11 */
"There's " + prop("Number") + " members." /* Output: "There's 12 members." */
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Working with 3 or More Operands
Since add is a binary operator, it can only work on two operands – the objects which are being operated on (if – the ternary operator – is the only operator that works on three operands).
If you need to work with more than two operands, the shorthand + is by far the easiest way to do it.
4 + 3 + 6 + 9 /* Output: 22 */
add(add(4, 3), add(6, 9)) /* Output: 22 */
4.add(3).add(6).add(9) /* Output: 22 */
"King" + " of the " + "Pirates" /* Output: King of the Pirates */
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Example Database
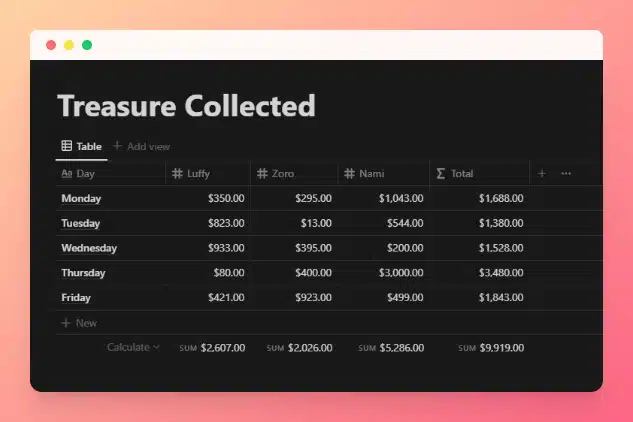
The example database below tracks a week of treasure-collecting by three pirates. The Total formula adds up all the treasure gathered by the three pirates collectively.
View and Duplicate Database

Note how I’ve set the number format of each column to U.S. Dollar. I’ve also set each column’s Calculate value to Sum, allowing me to see the total of all rows put together.
“Total” Property Formula
prop("Luffy") + prop("Zoro") + prop("Nami")
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Instead of using hard-coded numbers, I’ve called in each property using the prop() function.


