Database filters in Notion can target any type of property, including formula properties. However, there are some important rules to understand about how formulas and filters interact.
This page will explain those rules, and hopefully help you understand Notion’s limitations when combining filters and formulas.
Here’s the TL;DR version:
- Filter options for formula properties depend of the data type of your formula output (string, number, Boolean/Checkbox, date, list, person, or page).
- Formula properties are read-only.
- A formula filter will prevent a new row from being inserted into current view unless the filter fits the default output that formula would already have.
- In other words, formula filters cannot act as forcing functions. They cannot change the output of the formula. Formula output is determined solely by the formula itself and the variable data within any properties the formula references.
- Created by, Create time, Last edited by, and Last edited time properties are initially empty. This can cause confusion when filtering by them, or by formulas that reference them, so it’s good to understand this bit of nuance.
If you’d like to learn more about how to use filters in Notion databases, check out the filter section in my databases guide:

Example Database
All of the concepts explained in this article can be seen at work in this example database, which contains several unique views. Each view filters by one or more formulas.
View and Duplicate Database

Target a Formula with a Filter
Creating a filter that targets a formula property is no different than creating any other kind of filter.
You can create either a basic or advanced filter; either way, simply choose the formula property you want when setting up the filter:
Notion’s filter builder treats formula properties differently depending on the data type of their output.
Formulas that output strings are treated like text properties.
Options include:
- Is
- Is not
- Contains
- Does not contain
- Starts with
- Ends with
- Is empty
- Is not empty
Formulas that output numbers are treated like number properties.
Options include:
- = (equal)
- ≠ (not equal)
- > (greater than)
- < (less than)
- ≥ (greater than or equal to)
- ≤ (less than or equal to)
- Is empty
- Is not empty
Formulas that output dates are treated like date properties.
Options include:
- Comparisons:
- Is
- Is before
- Is after
- Is on or before
- Is on or after
- Is within
- Is empty
- Is not empty
- Dates:
- Today
- Tomorrow
- Yesterday
- One week ago
- One week from now
- One month ago
- One month from now
- Custom date
Formulas that output Boolean/Checkbox values are treated like checkbox properties.
Options include:
- Comparisons:
- Is
- Is not
- Choices:
- Checked
- Unchecked
In most aspects, a filter targeting a formula will behave exactly like a formula targeting another property type that outputs the same type of data.
However, this is one major difference: Formulas are read-only!
This has two major implications:
- You cannot create a forcing function that influences the output of a formula property.
- If your filter does not match the initial value of the formula, new rows will open directly as pages. They may also not show up in the database view that contains that filter.
The term “initial” is important in that latter point because the Created by, Created time, Edited by, and Edited time properties have a little-known quirk: Notion initially sees them as empty when a new row is created!
Likewise, any formula that references a property that has one of these types will also start off empty from Notion’s perspective.
The time/person is filled in so quickly that users never perceive this, but it does have important implications for filter design. Click here to go to the section of this article that’s about this quirk.
Formulas are Read-Only Properties
The most important thing to understand about formula properties in Notion databases is that they are read-only properties.
This means that you cannot click into a formula and directly change that formula’s output on a per-database-row basis.
In each database row, the return value of a formula property is determined solely by:
- The underlying formula – a.k.a. the “code” that you’ve entered into the formula editor
- Any properties which the formula references
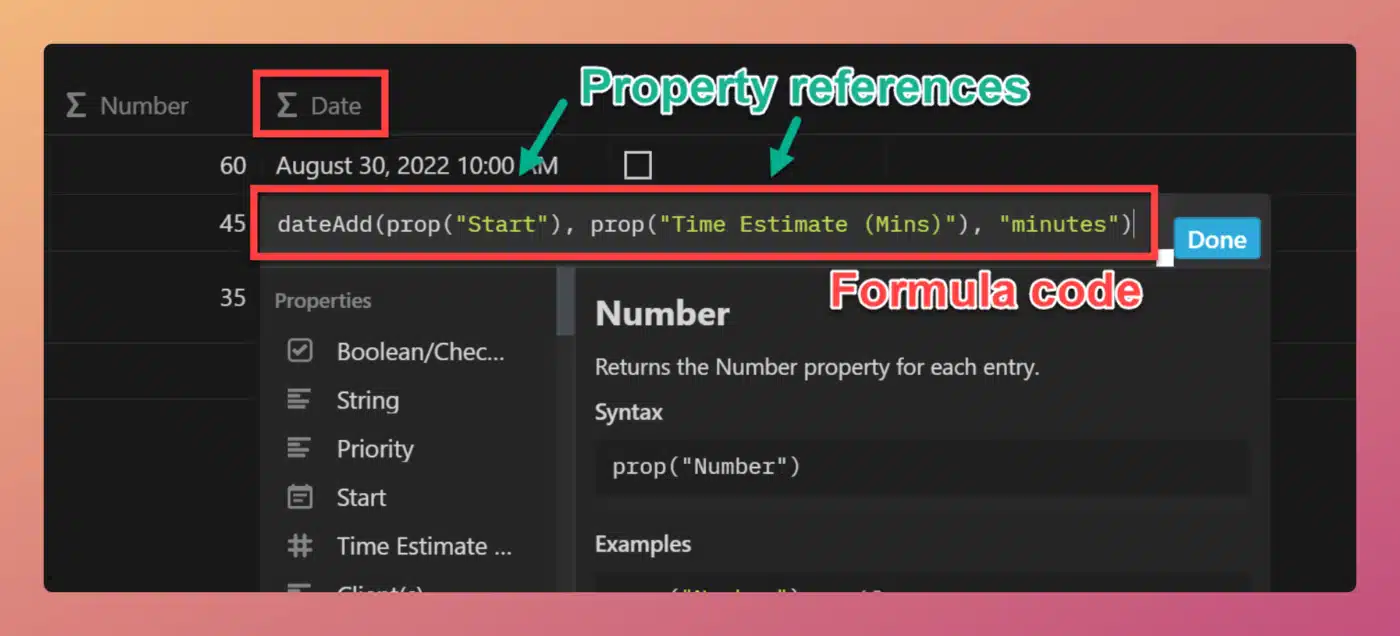
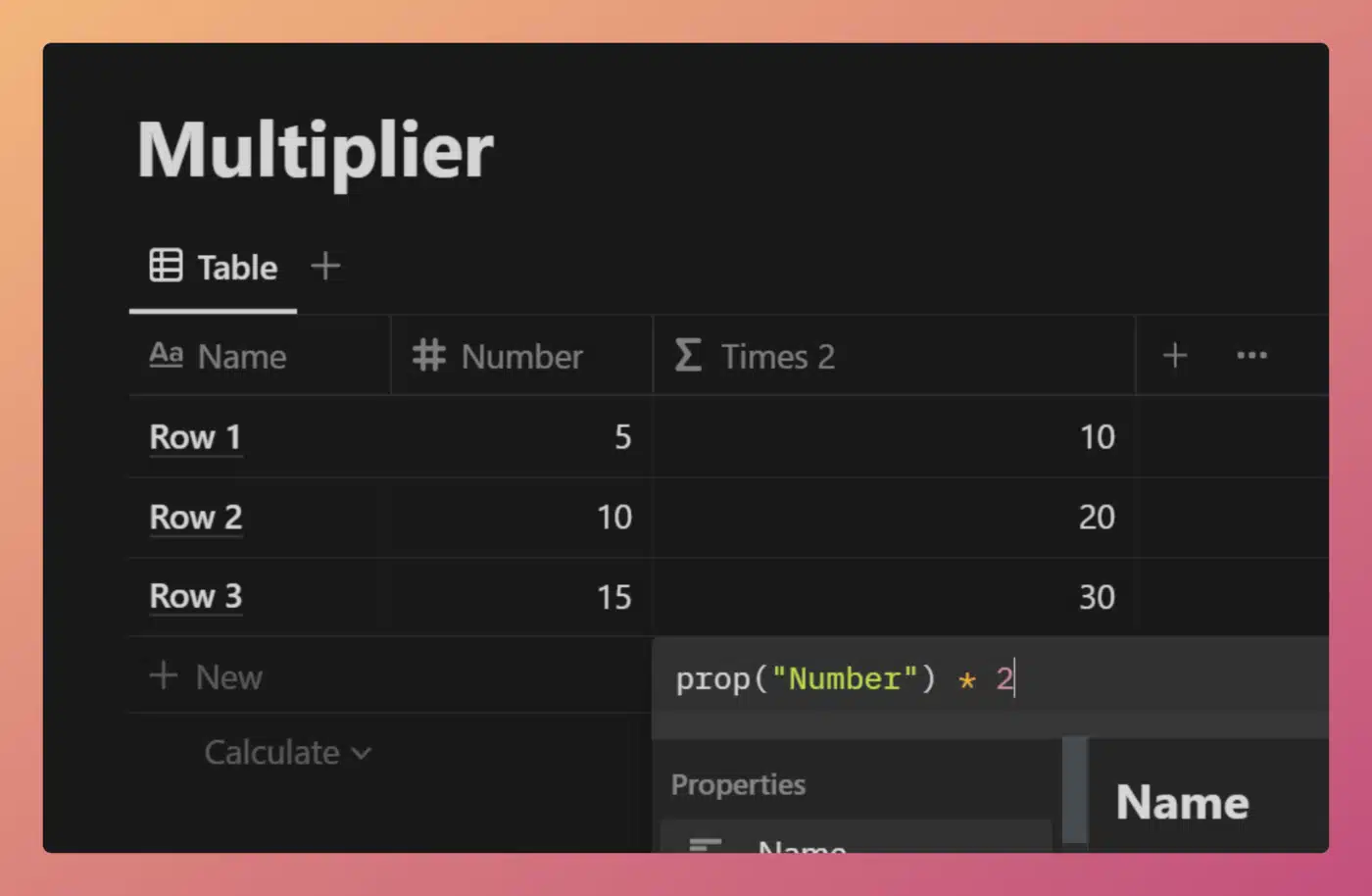
Formulas can have variable results on a per-row basis only when writable properties they reference contain variable data.
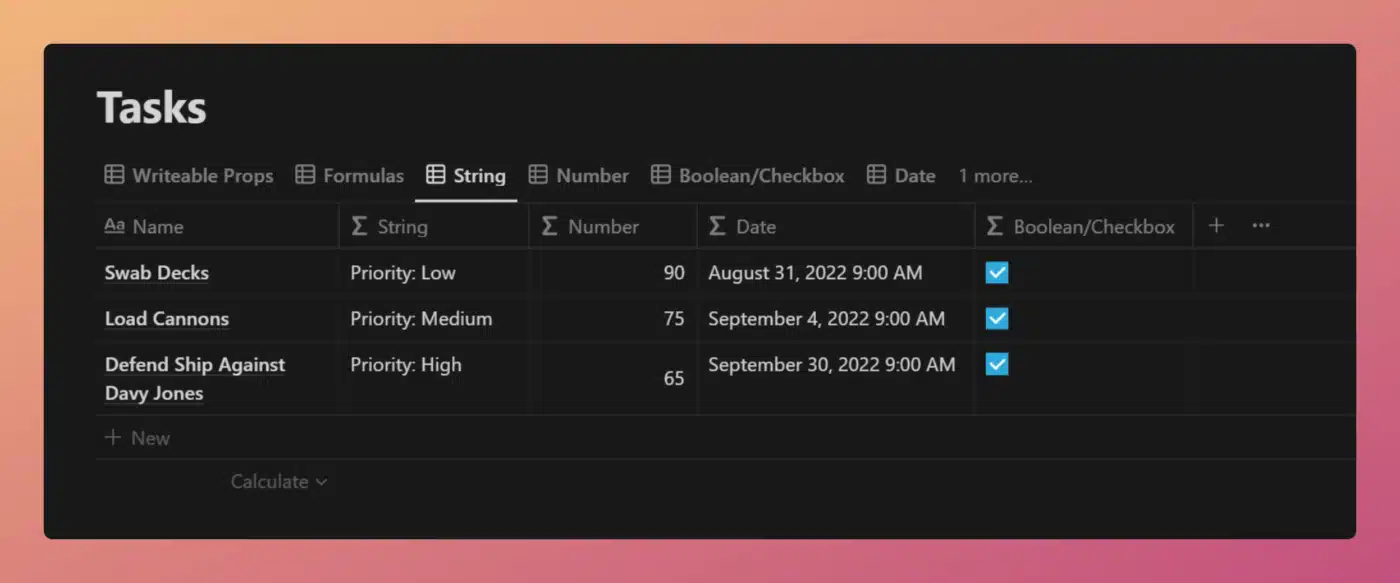
Consider this formula:
/* Property name: Times 2 */
prop("Number") * 2
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)This formula takes the value of the Number property and multiplies it by 2. Let’s say we have three database rows, with the following Number property values:
- 5
- 10
- 15
The formula’s output for these rows will be, respectively:
- 10
- 20
- 30
Now that you hopefully understand this concept, let’s cover the first major rule of formula/filter design.
Filters Must Match Default Formula Output for New Rows
If you’re designing a database view in which new rows do not need to be created directly, then this section isn’t important.
Example: You’re creating a “reporting” view for a database. This view simply gives you information about rows that have already been created in other views. In this case, set your filters however you want.
However, in many database views, you want to retain the ability to create new rows directly in the view.
To retain this ability, your filter critiera must match the default output that the formula would have. In other words, the filter cannot attempt to change the output of the formula.
Filters cannot act as forcing functions, applying specific values to formula properties.
Good to know: It’s worth noting that they also cannot do this for any read-only property type, including Rollup, Created by, Created Time, Last edited by, and Last edited time (additionally, they can’t set a non-empty value on a Files & Media property).
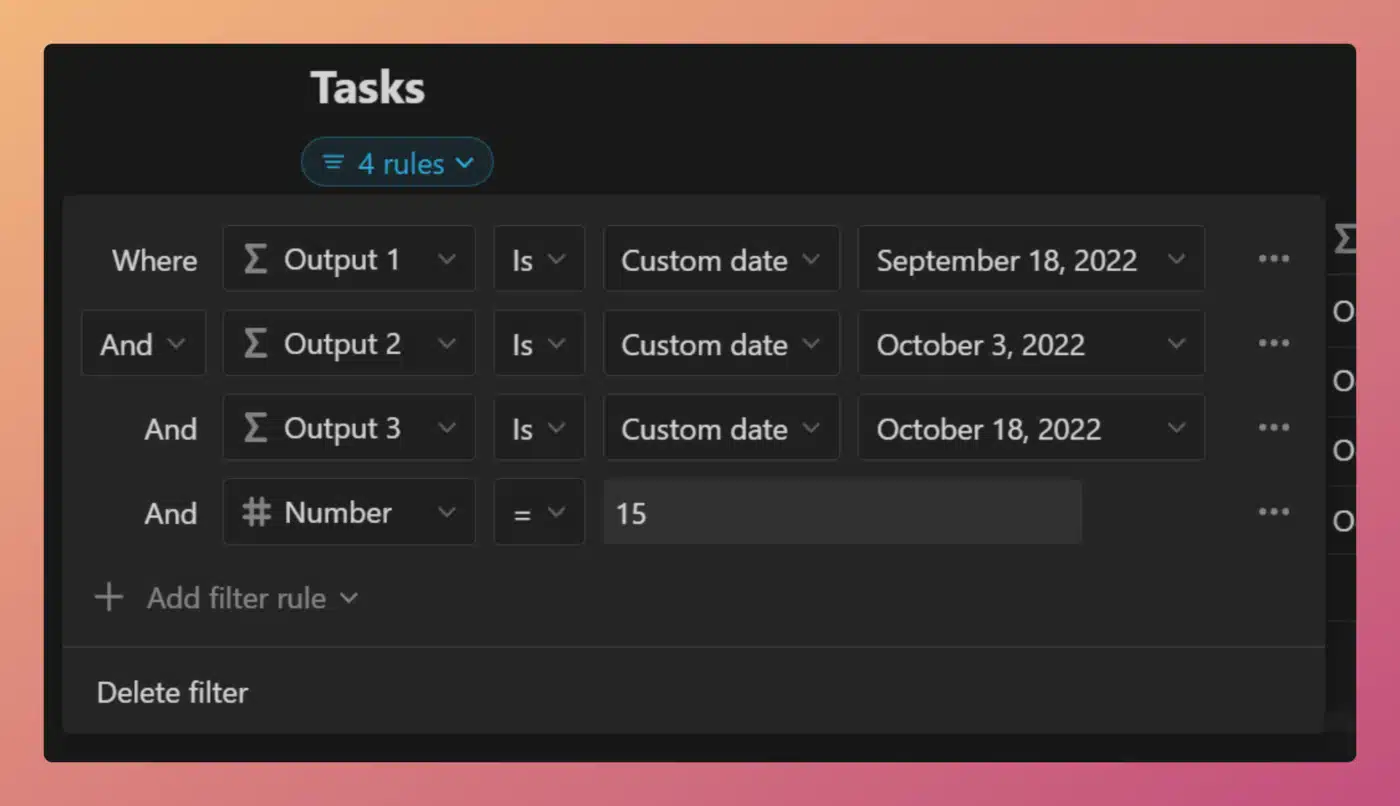
Here are a few examples of formulas (one for each data type), along with a valid and invalid filter for each. Again, this is only important in views where you want to be able to directly create new rows that stay in the view.
String Example
/* Property name: Priority */
"Priority: " + prop("Priority")
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Valid: Priority contains “Priority:”
- Invalid: Priority is “The Priority:”
Note how the invalid filter is looking for output that the formula doesn’t output by default.
Number Example
/* Property name: Timestamp */
timestamp(now())
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Valid: Timestamp > 0
- Invalid: Timestamp = 0
Boolean/Checkbox Example
/* Property name: Truth */
if( 10 > 5, true, false)
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Valid: Truth is checked
- Invalid: Truth is unchecked
Date Example
/* Property name: One More Day */
dateAdd(now(), 1, "days")
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Valid: One More Day is Tomorrow
- Invalid: One More Day is Today
List Example
Coming soon.
Person Example
Coming soon.
Page Example
Coming soon.
Formula Cannot Change Referenced Property Values
It’s worth noting that a filter/formula combination cannot influence or change the output of a property that is referenced within that formula.
What does this mean? Let’s go back to our multiplier example. The formula there is:
/* Property name: Times 2 */
prop("Number") * 2
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Here, I cannot simply create a filter like:
- Times 2 = 30
Notion will not automatically set the Number property’s value to 15 in order to make the Times 2 formula property return 30.
For this to work, you’d need two filters:
- Number = 15
- Times 2 = 30
However, at this point you do not need the filter for Times 2. If Number is set to 15 via a forcing function, then Times 2 will be 30 by default. Therefore, its filter is redundant.
Formulas are “Empty” at Initialization
In Formulas 1.0, formulas were faster to initialize than filters were to read their output. This mean that if you filtered on a formula value that would be on any new page by default (e.g. 1 == 1 returning true), table rows would come in as normal.
In Formulas 2.0, the formula property is “empty” for slightly longer. Not long enough for humans to tell, but long enough that filters see all formula properties as returning empty during the split-second when the db view’s filters check them upon new page creation.
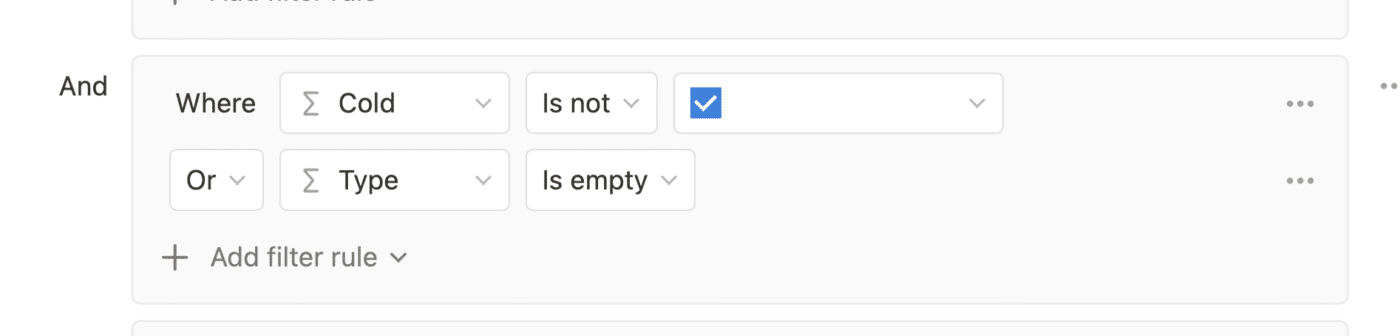
For this reason, any filter on a formula value needs to be paired with an “or” condition that will be satisfied during that split-second moment. Pictured is an example of that: Type is another formula, and so it’s empty for that split second.