The greater than (>) operator returns true if its left operand is greater than its right operand. It accepts string, numeric, date, and Boolean operands.
number > number
string > string
Boolean > Boolean
date > date
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Example Formulas
2 > 1 /* Output: true */
42 > 50 /* Output: false */
"b" > "a" /* Output: true */
/* Boolean values equate to 1 (true) and 0 (false). */
true > false /* Output: true */
true > true /* Output: false */
/* For dates, "less than" equates to "before". */
now() > dateSubtract(now(), 1, "days") /* Output: true */
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Good to know: When comparing dates, “greater” = “later”.
Good to know: The greater than (>) operator cannot be chained in a Notion formula. A formula like 3 > 2 > 1 won’t work. Use the and operator to get around this – e.g. 3 > 2 and 2 > 1.
Example Database
This example database records the power levels of two fighters at different stages. The Stronger formula outputs a sentence stating who the stronger fighter is at that time.
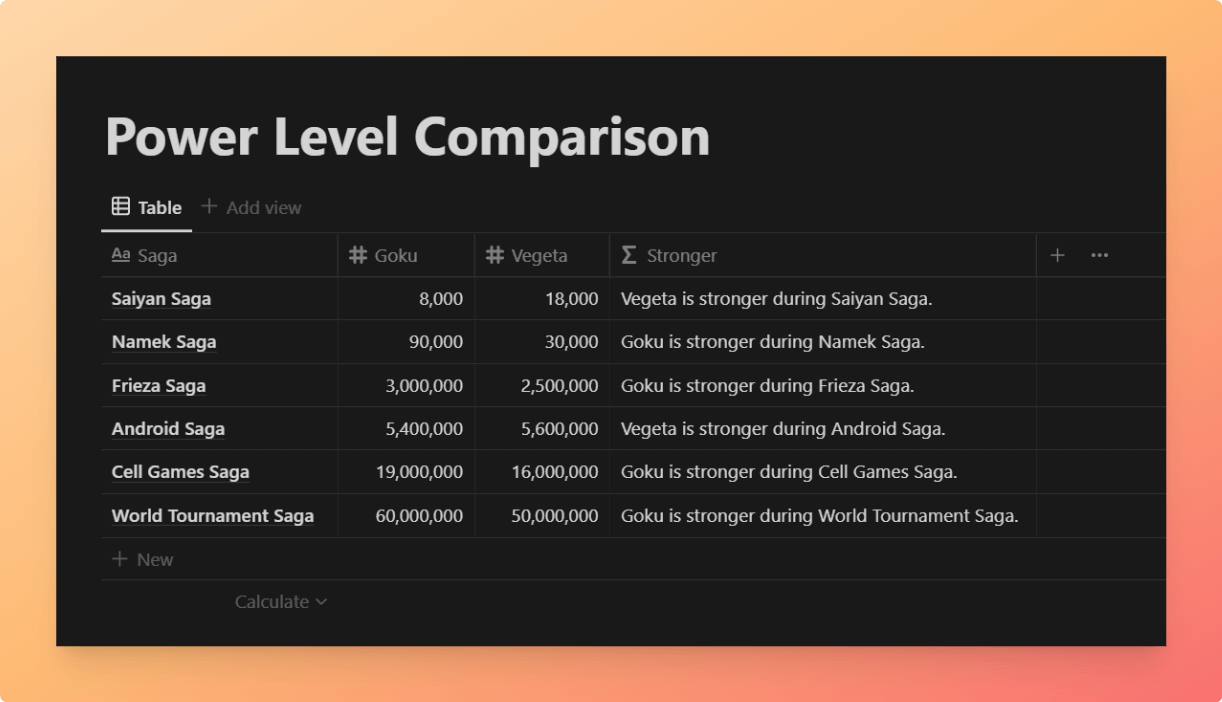
View and Duplicate Database

“Stronger” Property Formula
((prop("Goku") > prop("Vegeta")) ? "Goku is stronger" : "Vegeta is stronger") + " during " + prop("Saga") + "."
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)This formula uses the conditional operators ? and : to form an if-then statement. The output is then combined with strings and the output of the Saga property via the add (+) operator (which can concatenate strings).
Other formula components used in this example:






